Refractive Errors
(Near-sighted, Far-sighted, and Astigmatism)Myopia
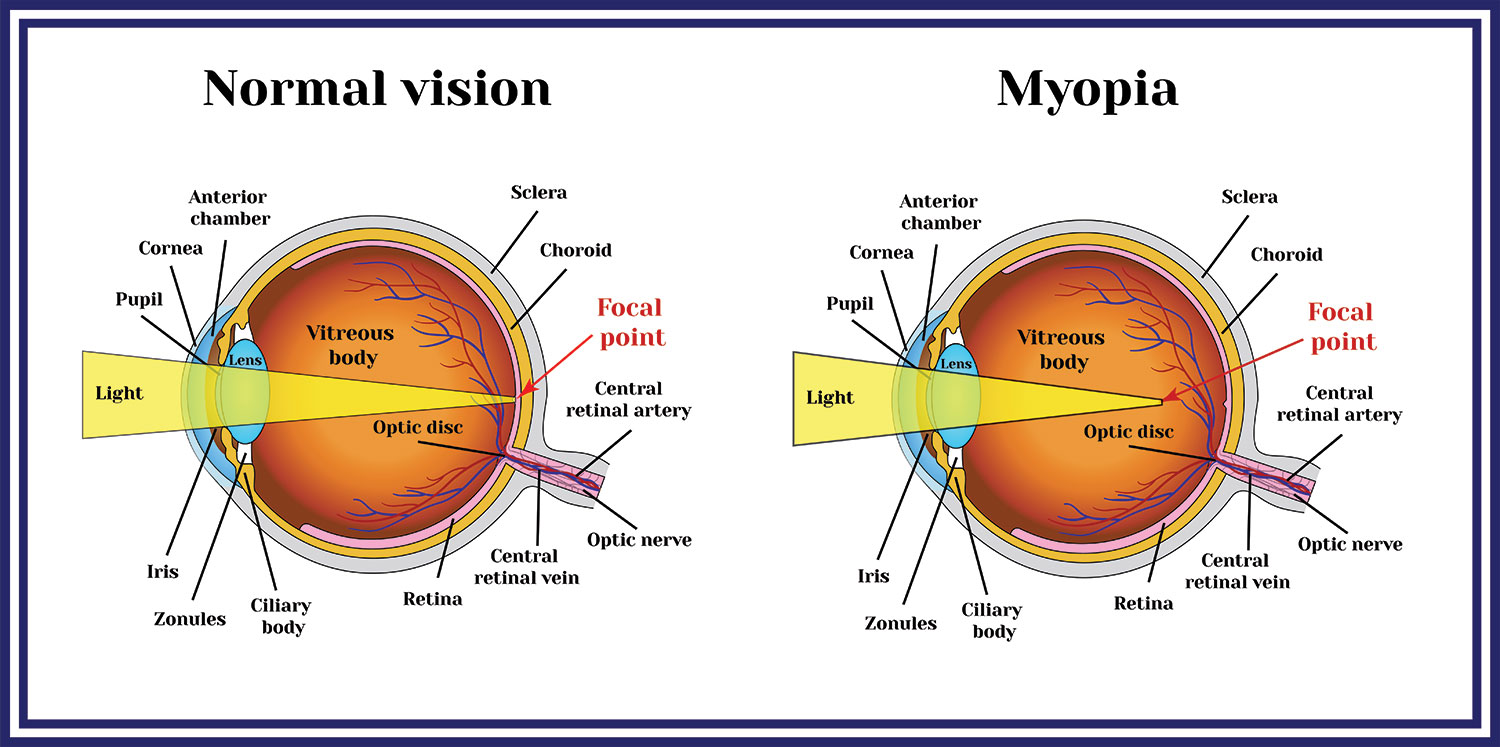
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness, is a condition when objects up close can be clearer than objects in the distance. Myopia results when the eye is “too long” or “too strong”, which causes light rays to focus in front of the retina. Myopia can cause difficulty with activities at a distance such as difficulty driving, watching television, or reading the board.
Hyperopia
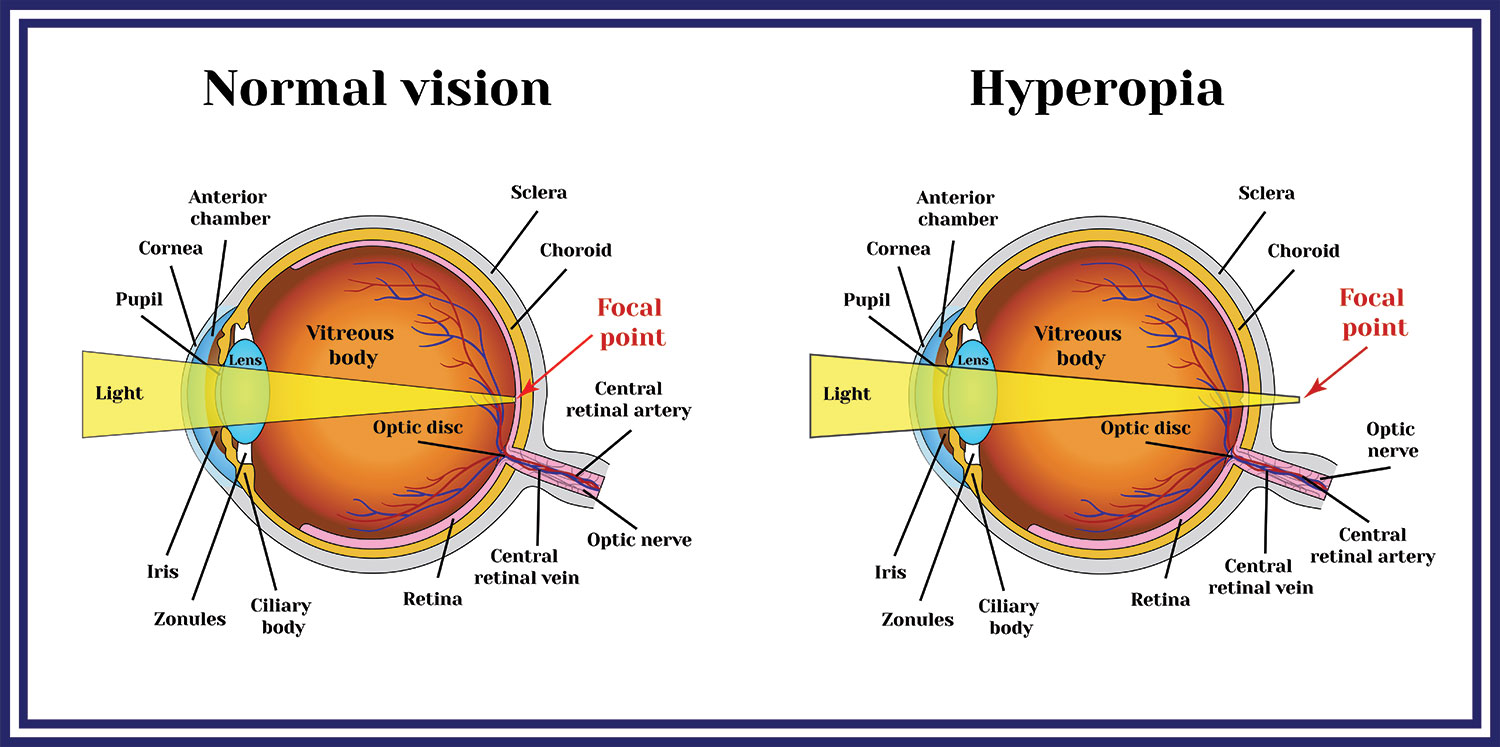
Hyperopia, or far-sightedness, is when objects at a distance can be clearer than objects up close. Hyperopia results when the eye is “too short” or “too weak”, which causes light rays to focus behind the retina. Hyperopia can cause difficulty with activities up close (reading, threading a needle), eye strain, and headaches (especially after prolonged reading or computer work). Though hyperopia is typically referred to as “far-sighted” not all people with hyperopia can see clearly at a distance. If the hyperopic prescription is too large then a person with hyperopia may not see clearly up close or at a distance.
Astigmatism
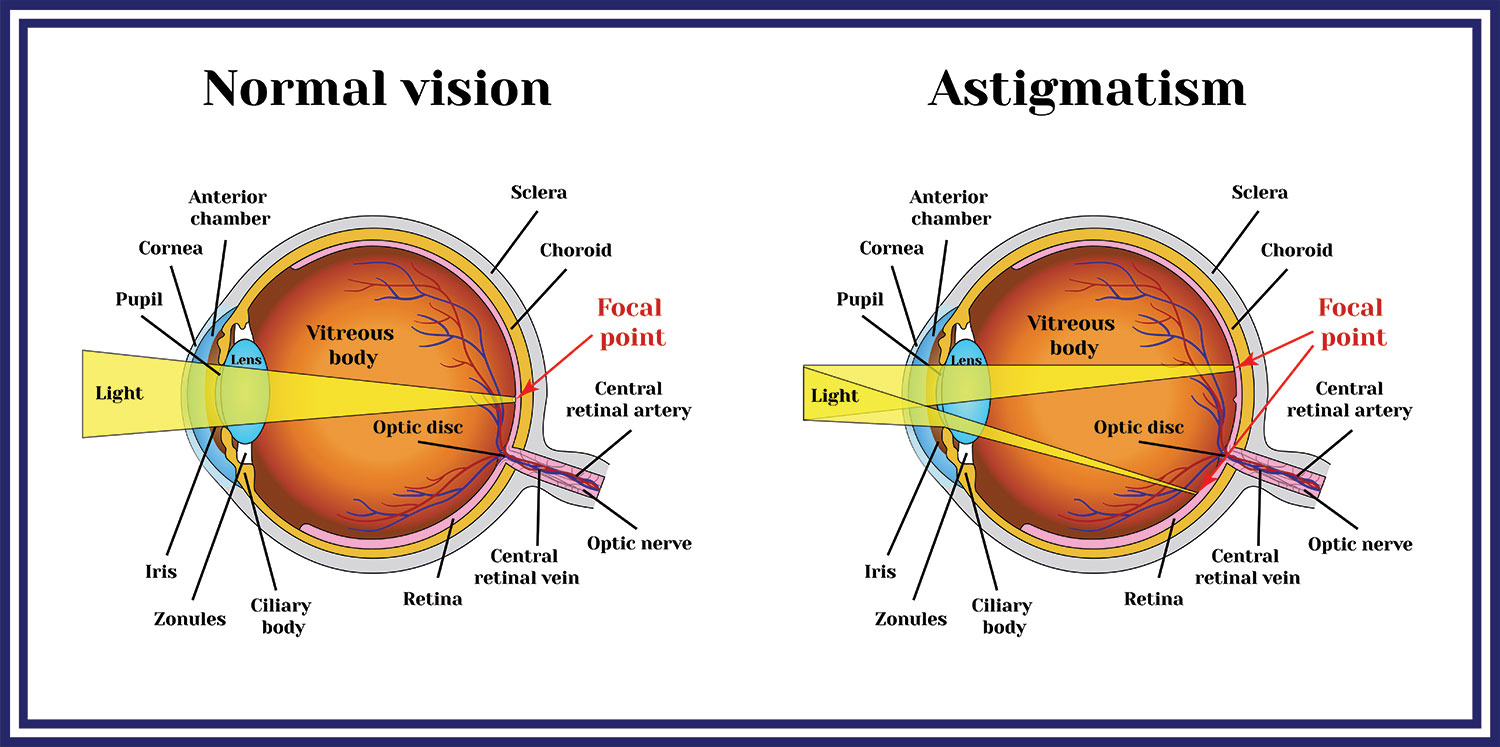
Astigmatism is a common condition caused by an irregularly shaped cornea which can cause blurry vision. Astigmatism can occur in conjunction with both myopia and hyperopia. Uncorrected astigmatism can cause strain, headaches, blurred vision, and halos or glare, especially at nighttime. Astigmatism is often worrisome to patients, but it can typically be corrected easily using glasses, or contact lenses.